To begin this article, let me first discuss what is iSCSI and then the reason for requiring an iSCSI.
I love the definition of iSCSI provided by searchstorage.techtarget.com which stands for Internet Small Computer System Interface, that works on top of the Transport Control Protocol (TCP) and allows the SCSI command to be sent end-to-end over local-area networks (LANs), wide-area networks (WANs) or the Internet.
According to the same site, iSCSI works by transporting block-level data from an iSCSI initiator on a server and a iSCSI target on a storage device. The iSCSI protocol encapsulates SCSI commands and assembles the data in packets for the TCP/IP layer. Packets are sent over the network using a point-to-point connection.
The one of the main reason for using iSCSI connections is that it allows for the utilization of existing network resources such as NICs and network switches to present storage devices to servers once it has the iSCSI initiator software. this result in cost saving and it is is easily configured and it is available for both LAN, WAN and internet which mean easily access if it is relocated to the cloud
Now, let us go to the fun part…configuration of iSCSI in Vmware ESXi 5.5
It is important to note that there are two type of iSCSI initiator/target:
- Software
- Hardware
In this article, we are only going to go through the configuring of the Software iSCSI initiator from within the VMware Esxi 5.5 hypervisor.
Log into vSphere Web client
Select Host and Clusters

Select the host you want you want to setup the the iSCSI Software adapter on.
Under the Host pane, select the Manage
Under Manage, Select Storage then Storage Adapters

Select the Plus button
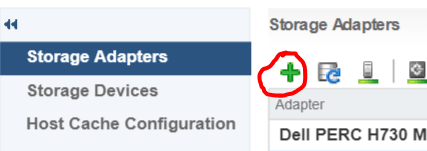
Select Software iSCSI Adapter
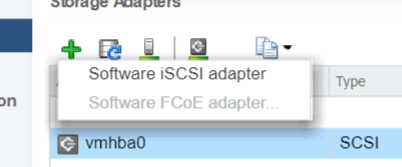
Select OK to the following message

Under Storage Adapters list, look for iSCSI Software Adapter and you will see the iSCSI Software Adapter listed.
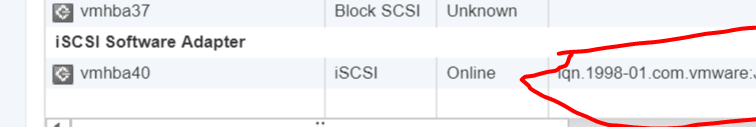
Highlight the adapter vmhbaXX (e.g. vmhba40) and under Adapter Detail, select Target –> Dynamic –> Add

Note: this allows you to add the primary IP address of the SAN or storage which allows the device LUNs to be discovered.
Enter the IP address of the target and leave the default port of 3260 for ISCSI communication. Then Select OK. For every iSCSI target, the IP address should be added.














