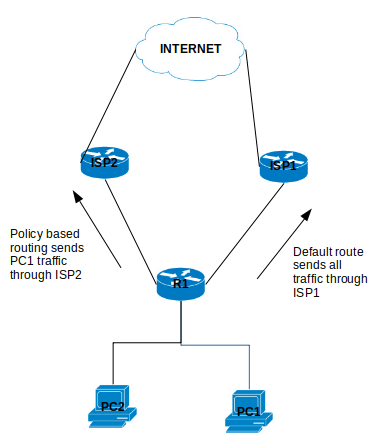
Policy-based routing (PBR) is a process whereby the device puts packets through a route map before routing them. (Cisco Reference)
Policy Based Routing is applicable to scenarios where you want to route a source IP address through a specific gateway IP address to a specific destination. Policy Based Routing relies on route-map to performs it functions which then uses access-list or prefix list to identify the respective source or destination IP address.
Configure Policy Based Routing
Step 1 – Configure Access list
R1(config)# ip access-list standard PC1-INT
R1(config-access-list)# permit ip host [PC1-IPAddress] [DestinationIP-Subnet]
Step 2 – Configure the Route map
R1(config)# route-map ISP2-INT [Sequence#]
R1(config-route-map)# match ip address [ISP2-INT]
R1(config-route-map)# set ip next-hop [ISP2]
Step 3 – Apply the Route map on the inbound interface
R1(config)# interface f0/0
R1(config-f)# ip policy route-map ISP2-INT
That is it for the configuration example for the Policy Based Routing.
There are a number of points to note about PBR:
- The implicit deny at the end of the route-map does not drop the packet but allow the traffic to be routed but the normal routing table.
- There is an option to include a keyword “default” in the route-map set parameter which tells the router to check the routing table for this destination address before apply the next hop:
- set ip default next-hop [IPAddress]
- Match all parameter can be applied by not setting any match conditions in the route map.
This is it for the Policy Based Routing and you can refer to Cisco documentation for further information.