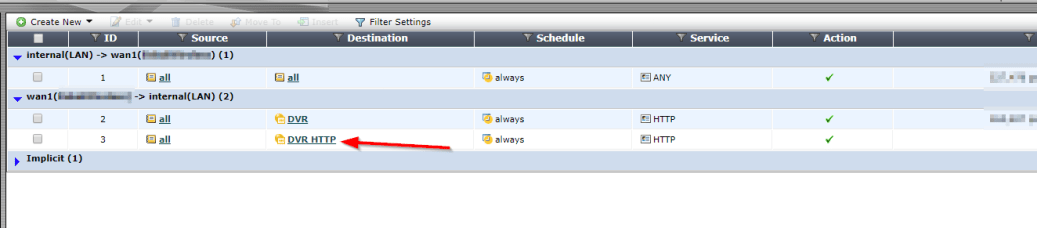
I had the privilege to learn another vendor’s switch configure from HP. This article will be about Configuring the following parameters in a HP 2530 similar what you will do in a Cisco access switch:
- Access port (edge port)
- Trunk ports (tagged port)
- Port security (MAC security)
- Ether channel (LAG)
- Spanning tree
- Portfast
- Enable secret password
- SNMP
- Switch virtual Interface (SVI)
- Vlan default gateway
- Show logging on the console
Before I begin we need to know that there are two main standards in the networking world, it is either Cisco or IEEE. So vendors like HP will only follow the IEEE standards. With that being said, let us begin:
What I am going to do is to show the Cisco way of the commands for the particular feature followed by HP.
1. Trunk ports: we know that Cisco switch has two protocol Used to develop a trunk port; ISL and 802.1Q (IEEE standard). Although the newest Cisco are no longer supporting ISL as it is being faced outed.
CISCO:
SW(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
SW(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
SW(config-if)# switchport trunk allow vlan 1-5
SW(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan 5
HP:
SW(configure)# int 49
SW(eth-49)# tagged vlan 1-4
SW (eth-49)# untagged vlan 5
2. Creating and configuring Voice vlan on a switch port that tells the IP Phone which vlan to use for communication.
CISCO:
SW(config)# interface f0/1
SW(config-if)# switchport voice vlan 6
HP:
SW(configure)# vlan 6
SW(vlan-6)#voice
SW(configure)#int 1
SW(eth-1)#tagged vlan 6
3. Configure Spanning-tree portfast to let the port transition into forwarding state immediately and also this configures the port as a access/edge port.
CISCO:
SW(config)# interface Fa0/1
SW(config-if)# switchport mode access
SW(config-if)# switchport access vlan 2
SW(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
HP:
SW(configure)# spanning-tree 1 admin-edge-port
SW(configure)# interface 1
SW(eth-1)# untagged vlan 2
4. Configure BPDU Guard to prevent a switch from connecting to a access port by shutting it down.
CISCO:
SW(config)#interface range fa0/1 – 24
SW(config-if-range)#spanning-tree bpduguard enable
HP:
SW(configure)# spanning-tree 1-24 bpdu-protection
5. Configure RSTP protocol to prevent loops in a network.
CISCO:
SW(config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
HP:
SW(configure)# spanning-tree
SW(configure)# spanning-tree force-version rstp-operation
6. Configure Port security using mac address restriction and limiting the number of devices connected.
CISCO:
SW(config)# interface range f0/1 – 24
SW(config-if-range)# switchport port-security
SW(config-if-range)# switchport port-security maximum 2
SW(config-if-range)# switchport port-security violation restrict
HP:
SW(configure)# port-security 1-24 learn-mode limited-continuous address-limit 2
7. Configuring SNMP on the switch for monitoring tool to access the switch status.
CISCO:
SW(config)# snmp-server community [string-password] ro
HP:
SW(configure)# no snmp-server community public
SW(configure)# snmp-server community [string-password] restricted
8. Configure username and password on the switch.
CISCO:
SW(config)# username admin privilege 15 secret [password]
HP:
SW(configure)# password manager user-name [admin] plaintext [networkpassword]
9. Configure Etherchannel or Link Aggregation (LAG) port to bundle two or more ports together. Remember that LACP is the standard protocol for other vendors except Cisco.
CISCO:
SW(config)# interface range Fa0/47 – 48
SW(config-if-range)#channel-protocol lacp
SW(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode active
HP:
SW(configure)# trunk 47-48 trk1 LACP
10. Configure Switch Virtual Interface IP address and default gateway.
CISCO:
SW(config)# ip default-gateway 10.1.1.1
SW(config)# int vlan 1
SW(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.10 255.255.255.0
SW(config-if)# no shutdown
HP:
SW(config)# ip default-gateway 10.1.1.1
SW(config)#int vlan 1
SW(vlan-1)#ip address 10.1.1.10 255.255.255.0
11. Show logging on the console
Cisco:
SW(config)# terminal monitor
HP:
SW# debug destination session
SW# debug event