This article will demonstrate how to install and configure the Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) and the Certification Authority (CA) using both the Server Manager and corresponding Powershell cmdlet.
Using Powershell method
Check if the Active Directory Certificate Service is installed
Get-WindowsFeature AD-Certificate
To install the Certification Authority features, run the following cmdlet:
Install-WindowsFeature ADCS-Cert-Authority -IncludeManagementTools
Configuring the Active Directory Certificate Services with a Standalone Root CA on Host1.
Install-ADcsCertificationAuthority –Credential (Get-Credential) -CAType [StandaloneRootCA] –CACommonName“domain-Host1-CA-1” –CADistinguishedNameSuffix “DC=domain,DC=com” –CryptoProviderName“RSA#Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider” -KeyLength 2048 –HashAlgorithmName SHA1 –ValidityPeriod Years –ValidityPeriodUnits3 –DatabaseDirectory “C:\windows\system32\certLog” –LogDirectory “c:\windows\system32\CertLog” –Force
You can select the CA Type by setting the parameter for –CA Type to either StandaloneRootCA, StandaloneSubordinateCA, EnterpriseRootCA or EnterpriseSubordinateCA. For the CA options like the Cryptographic Provider, Hash Algorithm and Key length will have to be known so that it is selected correctly.
Example for the key length, the values can be 512, 1024, 2048, 4096 which has to be typed out.
For Hash Algorithm, the options are: SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, SHA1, MD5, MD4, MD2.
For the Cryptographic Provider, the parameter -CryptoProviderName can be:
- RSA#Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider
- ECDSA_P521#Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider
- ECDSA_P256#Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider
- ECDSA_P384#Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider
- DSA#Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider
and any other…
Removing the AD CS and CA feature from the server.
Remove-WindowsFeature ADCS-Cert-Authority
Using the Server Manager
Go to Server Manager–> Manage –> Add Role and Features

Select Role-based or feature-based installation

Select the Server to install it on

Tick the Active Directory Certificate Services

Tick the Certification Authority
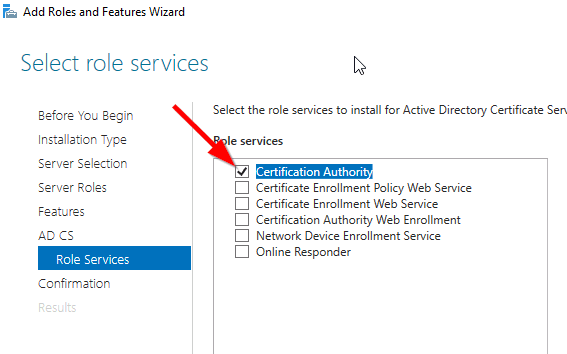
The feature will be installed and then you can select Configure Active Directory Certificate Services to setup the CA.

Enter the Credential that have permission to configure the CA. Note the following:
For Standalone CA: you need local administrator rights
For Enterprise CA: you need Enterprise Admin rights

Select role services: Certification Authority (CA)

select Standalone CA. Once you know how to configure Standalone CA then you can easily configure Enterprise CA.
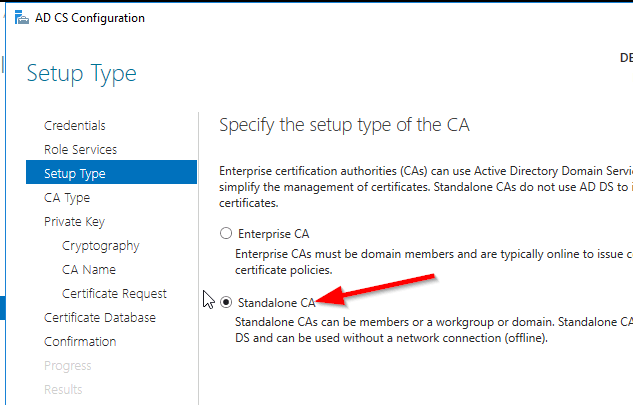
Select Root CA (this is the first CA)
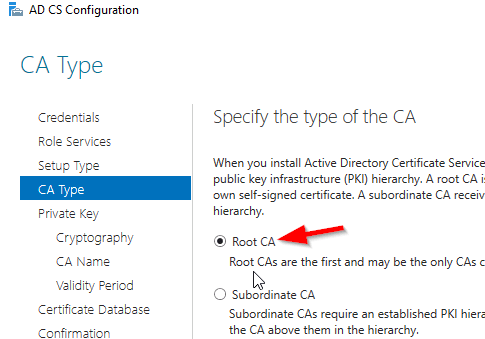
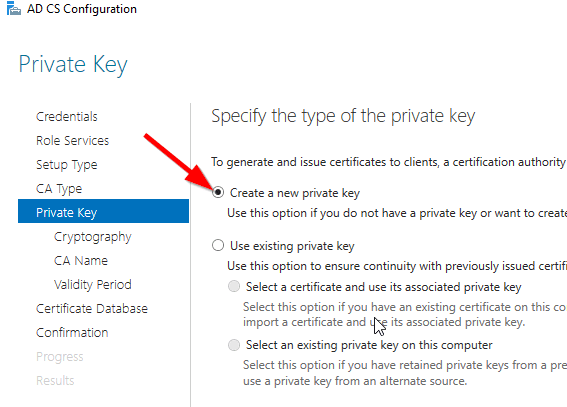
Select Create a new private key.
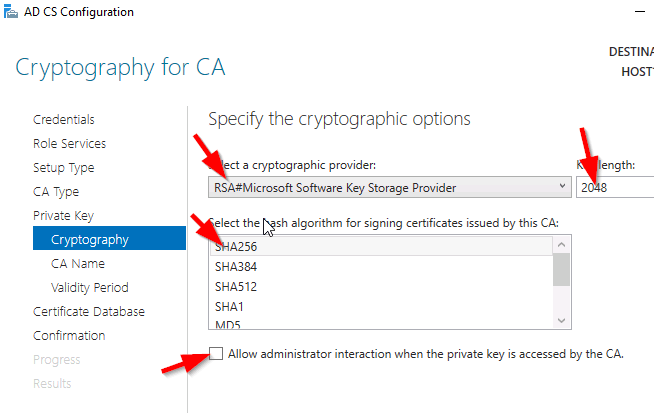
Select your preferred cryptographic provider, key length and hash algorithm
The Common Name and distinguished name suffix will be generated but you can enter your own name.

Select the validity period for the Certificate generated.

You can change certificate database and log path or let it remain at the default path

Confirm configuration settings of CA.

Once the CA installation is complete, you can go to Server Manager –> Tools –> Certification Authority to view CA server in the MMC.