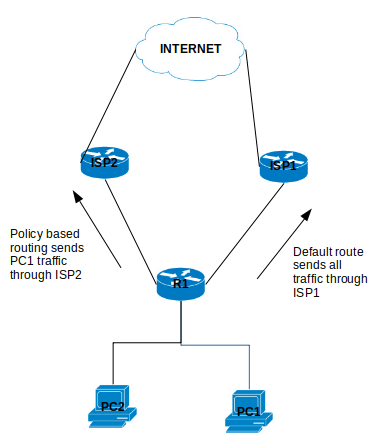
This article was written about OSPF as I prepare for the CCNP. It was be updated as I progress.
OSPF is the acronym for Open Shortest Path First which is a vendor mutual routing protocol.
- Shortest Path First SPF Algorithm for calculating the cost.
- Default hello timer: 10 seconds
- Default dead timer: 40 seconds (4 x hello)
- Multicast address: 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6
- Communication Protocol:
- Administrative distance of 110
- Process ID is local significant and is not required to be the same with the neighbors.
- The router ID is set using the following method in order:
- using the router-id command
- the highest IP address on the active loopback interface
- The highest IP address on the active physical interface
- Link State Updates (LSU) send every 30 minutes
OSPF neighbor relationship
OSPF States
Down –> Init –> 2Way –> ExStart –> Exchange –> Loading –> FULL
OSPF Packet Types
Type 1 – Hello
The purpose is to maintain the neighbor relationship using it as a keepalive.
debug ip ospf events of packet type 1
Wireshark capture of packet type 1.
Type 2 – Database Description (DBD)
debug ip ospf events of packet type 2
Wireshark capture of packet type 2
Type 3 – Link State Request (LSR)
debug ip ospf events of packet type 3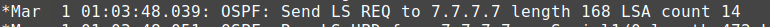
Wireshark capture of packet type 3
Type 4 – Link State Update (LSU)
debug ip ospf events of packet type 4
Wireshark capture of packet type 4
Type 5 – Link State Acknowledge (LSAck)
debug ip ospf events of packet type 5
Wireshark capture of packet type 5
OSPF Network Types
- Loopback – Stub Host – /32
- P2P – Point-to-Point – HDLC
- Broadcast – FastEthernet – DR/BDR
- NBMA -Non-Broadcast Multi Access
- P2MP – Point-to-Multipoint –
- Virtual Links
OSPF Area and Router Types
ASBR – Autonomous System Border Router
ABR – Area Border Router
Stubby Area
Totally Stubby Area
Not-So Stubby Area