I enjoying using powershell so I started to explore the possibility of using it for manipulating vSphere. Low and behold, welcome to PowerCLI with similar syntax as powershell or it can be called powershell in vSphere.
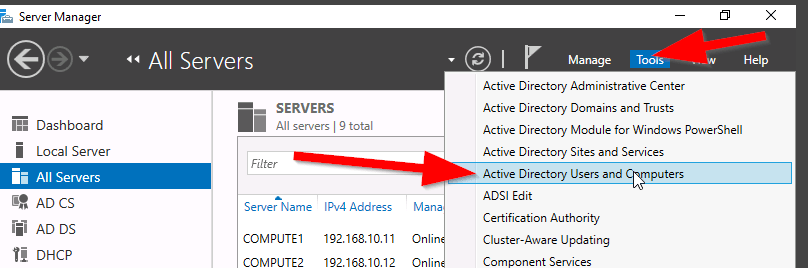
Firstly, before the vCenter server can be manage, a connection is required. To do so, this command can be executed. It can also be used to connect to a single ESXi Host.
Connect-VIServer [vCenterServer or ESXiHost] -Credential(Get-Credential)
I prefer to use the Get-Credential cmdlet because it will prompt me with a windows dialog box requesting the username and password (It is a very useful cmdlet).
Once connected, to get the List of Cluster , VM or Host the following respective commands can be used:
Get-Cluster
Get-VM
Get-VMHost
To get specific details the name of the object can be added to the cmdlet. The pipe (|) can also be used to get details from specific area.
Example to retrieve all the Virtual machines within Cluster A
Get-Cluster ClusterA | Get-VM
To Get all VMs on ESXi Host A
Get-VMHost ESXiA | Get-VM
Putting an ESXi Host A in Maintenance mode
Set-VMHost ESXiA -State Maintenance
Shutting down the ESXi Host A
Stop-VMHost ESXiA-Force
Startup Virtual machine VM1 and VM2
Start-VM VM1,VM2
Exit Maintenance Mode for ESXi Host A
Set-VMHost ESXiA -State Connected
To get more cmdlet from the VMware PowerCLI, use the get-command [*keyword*] to list all commands with the keyword.
I will update this list as time progress.